Process of phlebotomy involves handling of infectious items such as Blood, Urine and other body fluids & secretions along with generation of potentially dangerous biomedical wastes like used infected Sharps and other consumable waste. Hence Phlebotomy design should also inculcate the best practice guideline on Bio-safety, biomedical waste management, and safety engineering controls as given by OSHA. The employer should also ensure that wherever possible phlebotomist are made available with personal protective equipment’s (PPE), safety-engineered device for sample collection and discarding.
The best phlebotomy setups embrace the proper use of technology and best available devices for safety and workflow improvement.
When we talk about laboratories, the goal is to provide accurate and timely reports; timely reporting is the function of good turnaround time in the laboratory i.e. the time from patient entering the lab to the time reports are generated. And TAT many a time is impacted by many non-value added activities which are done at the Phlebotomy centers. Best of labs pay special attention to the workflow improvement and process controls by studying the bottle-necks in the process and practices and Improving TAT. By having a lean phlebotomy workflow will also impact productivity and greatly increase the customer satisfaction, as patient waiting time for giving blood samples and wait for getting the reports will be reduced in lean labs.
It is also imperative that every phlebotomist working in the blood collection area along with staff Involved in processes like sample transport, specimen accession centrifugation and pre-processing of samples should be trained or made aware of Preanalytical errors, as documented the 60-70% of errors happening in the laboratory originate from Preanalytical phase of the lab (collection, handling, pre-processing, transportation and storage of samples). these errors have a greater impact on the final reports given to the patients.
Finally all the staff working in blood collection area should have periodic refresher training on topics like Preanalytical errors, Bio-safety, usage of device.
1. Design for patient and workers comfort
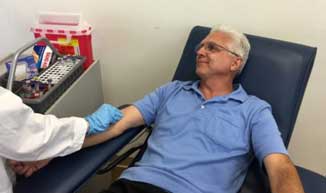
• Room should be large enough well-lit and ventilated.
• Proper waiting area for patients with enough space and comfortable waiting chairs.
• Easy to understand instructions (in patient’s language) to be given while registration with information on billing and report timings.
• Poster on awareness on blood test and pre-requisite for blood collection should be displayed so as to avoid confusion on states like fasting etc.
• Waiting time should be taken in context and should be displayed in form of token calling system for high workflow areas.
• Proper arrangements for drinking water and availability of eatables for diabetic patient in case of hypoglycemia.
• Provision for Washroom should be done within close proximity of phlebotomy room.
• Blood collection chair should be comfortable enough and it should accommodate all size of patients.
• Small examination beds should be available in case collection to be done for Paediatric or over apprehensive patient.
• The room should contain a refrigerator for specimens and one for refreshments. The room should have a freezer that holds a few ice packs that can be used in case a patient feels faint or if they bruise.
• The refreshment fridge should be stocked with orange/ apple juice / gluconate-D. There should also be biscuits/cookies on hand.
• It is advised to have an eyewash station within the blood collection room, so as the technician can immediately rinse the eyes in-case of any accidental splatter of blood or body fluids.
• First aid kit should be kept ready in phlebotomy room.
• Trays with covering lids labeled for urine and stool specimen should be placed outside the washroom.
2. Safety practice & engineering controls:
• At least one sink should be available in the phlebotomy room.
• Hand sanitizer should be close to the collection chair.
• Sharps containers should be wall mounted and attached on work table near blood collection chair.
• Each chair should have individual sharp containers and placed in such a way that no overlapping of the hands used should happen during disposal.
• Other non-sharp waste disposable bins should also be place in proximity with collection chair.
• Glove box should be placed on wall mount or on phlebotomy work table.
• All electrical wiring should be concealed and no open wire should be passing within the phlebotomy room.
• Proper poster on safety guidelines to be displayed in Phlebotomy area.
3. Process improvement and lean workflow

• Collection items should be kept at hands distance eg: in wall mount tube dispenser.
• All extra collection and post-collection items for should be adequately stocked in the work table ( eg: different types of avail tubes, needles, syringes, cotton, sprit, lancets, bandages, lancets, markers, urine containers etc)
• For pediatric specimen collection, proper pediatric collection assembly should be available .
• Use of barcode printing and identification will improve the TAT.
• Dispensing of urine cup/stool cup should be done at Phlebotomy chair itself post collection of a blood specimen.
4. Embrace the use of technology and proper devices over old practice
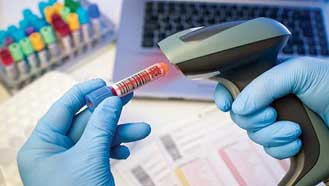
• Patient register → Computer and barcode system or Preanalytical auto tube labeler
• Patient waiting area → patient calling Token systems
• Normal chairs → reclining Phlebotomy chairs
• Needle cans → safety sharps containers
• Blood collection tubes → Evacuated blood collection tubes / pediatric tubes and lancets
• Syringe and Needles → Evacuated Blood Collection Multisampling needles
• Cotton and spirit → Alcohol Swabs
• Regular table → phlebotomy work table
• Regular bags → Cold chain specimen transport bags
5. Awareness of Preanalytical errors
• Available for display charts in phlebotomy area ( eg; order of draw, collection procedure, vein selection )
• Available SOP’s booklet for blood collection at the site
6. Troubleshooting guidelines to be available at the site
7.Certified and trained phlebotomist.

